Are you looking to get the most out of your generator? If so, you need to make sure you are using the best fuel for your generator. This article will help you discover the best fuel for your generator that will provide maximum efficiency and performance. Learn about the different fuels available and which one is the best for your generator.
What is a Generator?
A generator is an engine-powered device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It works by using a fuel source, such as gasoline, diesel, or natural gas, to turn a turbine or other mechanical device, which creates electrical current. Generators are used to provide power to homes, businesses, and other facilities in the event of a power outage, or to provide additional power when needed.
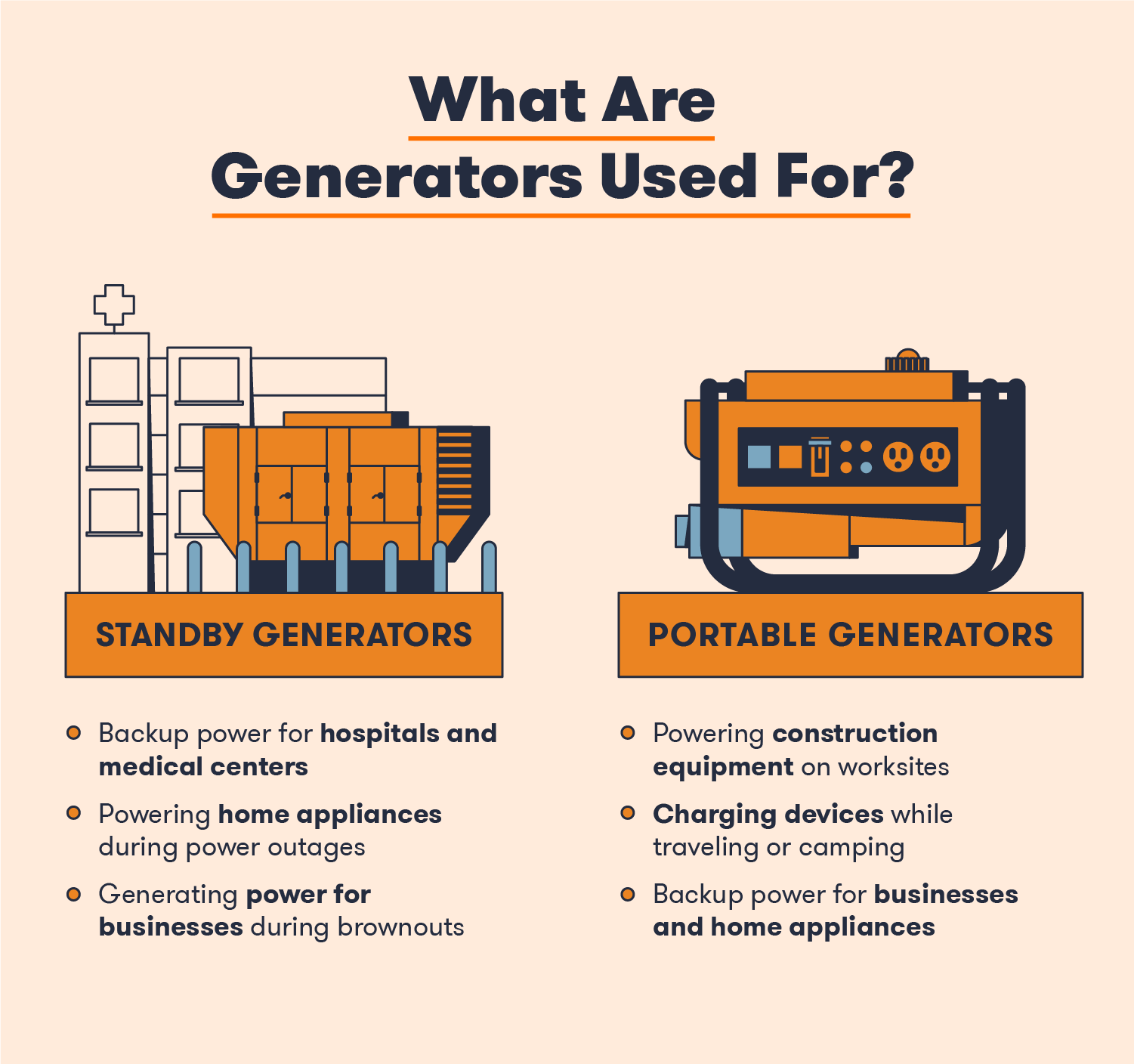
Types of Generators

| Type of Generator | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Portable Generators | Used to power small appliances such as laptops, lights and small tools |
| Standby Generators | Used to power entire homes or businesses during power outages or in remote locations |
| Inverter Generators | Used to provide power to sensitive electronics and devices |
| Towable Generators | Used to power large construction sites and events |
Portable generators are small and designed to be used in remote locations or during power outages. Standby generators are larger and designed to power entire homes or businesses in the event of a power outage. Inverter generators produce a clean energy source that is ideal for powering sensitive electronics and devices. Towable generators are large and designed to power large construction sites and events.
Gasoline


Gasoline is used in most portable generators, and is often the most readily available fuel source. It is easy to find and store, and is typically priced lower than other fuels. However, gasoline has a short shelf life and can degrade over time.
Diesel

Diesel generators offer a more efficient fuel source than gasoline. Diesel fuel is more stable and has a longer shelf life than gasoline, making it a good option for long-term storage. Diesel generators are also more fuel efficient than gasoline, making them a cost-effective option in the long run.
Propane

Propane generators are a great option for areas where natural gas is not available. Propane is clean burning and offers a longer run time than gasoline. It also has a longer shelf life than gasoline.
Natural Gas

Natural gas generators are the most efficient fuel source for generators. Natural gas is stable and has an indefinite shelf life. It is also the cleanest burning fuel source, making it the most environmentally friendly option.
Gasoline


Pros
Gasoline is the most commonly used fuel for generators, as it is widely available, inexpensive, and easy to store. It is also relatively easy to use, and its power output is relatively high.
Cons
Gasoline is highly flammable and has a relatively short shelf-life. It can also be dangerous to store in large quantities, and its exhaust can be extremely toxic.
2. Diesel
- Diesel is a cost-effective fuel for generators.
- It has a higher energy density than gasoline and produces less greenhouse gas emissions.
- Diesel is more efficient than gasoline, meaning it will last longer and reduces the amount of fuel needed for the same amount of power generation.
- Diesel generators are generally more reliable due to their durability and the simplicity of their design.
- Diesel generators are also more fuel efficient than gasoline generators.
3. Propane

| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Clean burning | More expensive than diesel |
| Higher octane rating | Easily flammable |
| Always available | Needs proper ventilation |
| Lower emissions | Propane tanks may need to be refilled |
Propane is a clean-burning fuel and has a higher octane rating than diesel. It is always available and produces fewer emissions than diesel. The drawbacks to using propane as a fuel include it being more expensive than diesel and easily flammable. Propane tanks may need to be refilled and proper ventilation is needed.
4. Natural Gas

- Can be sourced from the main gas supply line
- Clean burning fuel, with lower emissions than petrol and diesel
- Very efficient fuel
- Easily available
- Less expensive than petrol and diesel
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Generator Fuel

| Fuel Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Gasoline | Widely available; Cost-effective | High emissions; Flammable |
| Propane | Odorless; Non-toxic; Non-flammable | Costly; Needs to be refilled |
| Diesel | Cleaner burning; More efficient | Noisy; Costly |
| Natural Gas | Clean burning; Cost-effective; Easy to store | Requires a professional for installation; Limited availability |
When choosing a fuel for your generator, there are several factors to consider. Gasoline is the most widely available and cost-effective fuel option, but it is also highly flammable and produces high emissions. Propane is odorless and non-toxic, but it needs to be refilled regularly and is more expensive than gasoline. Diesel is a cleaner burning, more efficient fuel, but it is also noisy and more costly. Natural gas is clean burning, cost-effective, and easy to store, but it requires a professional for installation and may not be available in all areas.
Best Fuel for a Generator

- Gasoline: Gasoline is one of the most common and affordable fuels for generators. It is easy to find and is usually the fuel of choice for portable generators.
- Diesel: Diesel is a popular fuel for stationary generators due to its efficiency and low emissions. It is also a good choice for portable generators, although it can be harder to find and more expensive than gasoline.
- Propane: Propane is a clean-burning fuel that is ideal for both stationary and portable generators. It is readily available and often cheaper than gasoline or diesel.
- Natural Gas: Natural gas is a clean-burning, efficient fuel that is ideal for stationary generators. It is often the most economical option, but it is not suitable for portable generators.
- Biofuel: Biofuel is a renewable fuel made from plant or animal material. It is a clean-burning and eco-friendly fuel, but it can be expensive and hard to find.
Safety Considerations
- Never refuel a generator while it is running.
- Always keep a fire extinguisher handy when operating a generator.
- Never use gasoline to start a generator.
- Always ensure that the generator is in a well-ventilated area.
- Make sure to disconnect any appliances from the generator before refueling.
- Never attempt to repair or service a generator while it is still connected to an electrical source.
- Check the fuel line for any signs of leaks or damage before use.
- Make sure to use the correct type and grade of fuel for the generator.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring your generator runs properly and efficiently. To keep your generator running its best, you should check the oil level, air filters, and spark plugs regularly, and replace them when necessary. You should also inspect the fuel lines for leaks and ensure the fuel tank is securely sealed. Additionally, it is important to check the electrical connections and wiring regularly and to tighten any loose connections. Finally, it is important to keep your generator clean and clear of dirt and debris to reduce the risk of a fire hazard.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best fuel for a generator?
The best fuel for a generator depends on the type of generator and its intended use. For portable generators, gasoline is usually the most efficient and cost-effective fuel choice. Diesel fuel is an excellent choice for larger generators as it has a higher energy content than gasoline and is more reliable in extreme temperatures. Natural gas is also a popular fuel choice for larger generators due to its cost-effectiveness, low emissions, and ability to run for extended periods of time without refueling.
How can I get maximum efficiency and performance from my generator?
In order to maximize efficiency and performance from your generator, it is important to ensure that the fuel you are using is of good quality and is free of contaminants. The type of fuel used should be appropriate for the type of generator, and should be able to provide the necessary power output. Regular maintenance and servicing of the generator is also necessary to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Additionally, it is important to ensure that the generator is well ventilated and that the engine oil is replaced regularly.
What type of gasoline should I use in my generator?
Gasoline is the most common type of fuel used in generators. For optimal performance, it is important to use fresh, clean gasoline with an octane rating of 87 or higher and no more than 10% ethanol content. It is recommended to use gasoline that has been stored in a tightly sealed, airtight container and has been treated with a fuel stabilizer if it will not be used within 30 days. Additionally, it is important to use a fuel stabilizer every time you fill the generator tank to extend the life of the fuel.
How often should I change the fuel in my generator?
Fuel in your generator should be changed every 3-4 months, as it can begin to break down and become stale over time. This is especially important if the generator is used infrequently, as the fuel can become gummed up in the carburetor and cause a loss of power. Additionally, if you are using a gas generator, it is important to use a fuel stabilizer to prevent the fuel from breaking down.
What are the Benefits of Using the Best Fuel for my Generator?
Using the best fuel for your generator can result in improved engine performance, reduced emissions, and extended engine life. It can also help reduce the need for maintenance and repairs, as well as reduce fuel costs. Additionally, using the best fuel can help the generator run more efficiently and can provide a more reliable source of power.
Conclusion
Generators are essential pieces of equipment that provide power during outages. Choosing the right fuel for your generator is essential to ensure maximum efficiency and performance. Natural gas is often the best choice for long-term, consistent power, while diesel is more suitable for short-term, heavy-duty applications. Propane can be used for both short and long-term power needs, but it is generally used for short-term applications. The cost and availability of each fuel type should be taken into consideration when making a decision.






