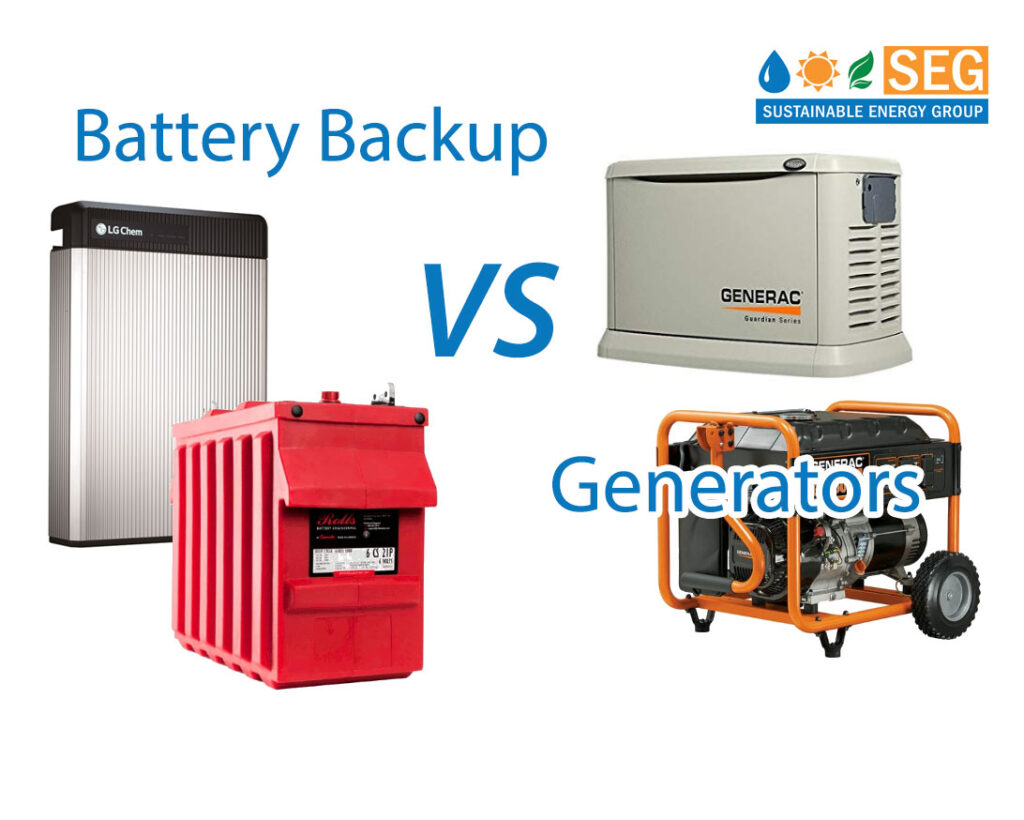
When it comes to portable power, the debate between batteries and generators can be quite heated. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, so it can be difficult to decide which is the better choice for your generator needs. In this article, we will take a closer look at the pros and cons of both battery and generator power and help you decide which is the best choice for your particular needs. We will discuss the differences between the two, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and the costs associated with each. By the end of the article, you should have a better understanding of whether a battery or generator is the better choice for your generator needs.
Overview of Generators
Generators are a reliable source of power and are typically used when there is no access to an electricity grid. Generators are available in a variety of sizes and power outputs, ranging from small portable models to large industrial-grade units. Portable generators are ideal for camping, RVing, and other outdoor activities. While larger stationary units are better suited for home and business use.
Generators are typically powered by either gasoline, diesel, or propane. Gasoline powered generators are usually the most cost-effective option, and are the most common type of generator. Diesel powered generators are more reliable and powerful, and are often used in industrial and commercial applications. Propane powered generators are more fuel-efficient and are best suited for emergency or backup power.
Generators can be used to power a wide variety of electrical appliances, from lights, fans, and TVs to air conditioners, refrigerators, and sump pumps. They can also be used to charge batteries, run tools, and power electric motors.
| Type | Fuel Source | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Portable | Gasoline | Camping, RVing |
| Stationary | Gasoline, Diesel, Propane | Home/Business use |
Types of Generators

Generators are classified into two distinct types: Internal Combustion (IC) and Electric. IC generators are powered by an internal combustion engine, such as a diesel or gasoline engine. Electric generators are powered by an electric motor.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Portable | Small, easy to transport generators typically powered by gasoline or diesel. |
| Standby | Permanently installed generator typically powered by natural gas or propane. |
| Inverter | Small, lightweight generators powered by gasoline, diesel, or propane. |
| Diesel | Heavy-duty generators typically used for industrial or commercial applications. |
| Turbine | High-capacity generators typically used for large commercial or industrial applications. |
Advantages of Generators

| Feature | Generator |
|---|---|
| Power Output | Generators can produce significantly higher power output than batteries. |
| Reliability | Generators are more reliable than batteries in most conditions. |
| Durability | Generators are more durable than batteries, and can withstand more extreme conditions. |
| Lifespan | Generators have a longer lifespan than batteries. |
| Maintenance | Generators require less maintenance than batteries. |
Disadvantages of Generators

- Cost – Generators can be expensive to purchase, install and maintain.
- Noise – Generators are typically loud, making them unsuitable for residential areas.
- Fuel Supply – Generators are dependent upon a fuel supply (e.g. gasoline, diesel, propane, etc.), which can be difficult to come by in some areas.
- Pollution – Generators produce emissions, which are harmful to the environment.
- Maintenance – Generators require regular maintenance and servicing to ensure they remain in good working order.
Overview of Batteries

| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-acid Battery | Low cost, long lifecycle, easy to maintain | Heavy and bulky, limited capacity |
| Lithium-ion Battery | Lightweight, high capacity, long cycle life | High cost, sensitive to temperature |
| Nickel-Cadmium Battery | Durable, reliable, low self-discharge rate | High cost, short life cycle, toxic |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride Battery | High energy density, low cost | High self-discharge rate, short cycle life |
Batteries are commonly used to store and deliver electrical energy. There are several types of batteries available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Lead-acid batteries are the most common type, and are typically used for automotive applications. They are relatively low cost, have a long lifecycle, and are easy to maintain. However, they are also heavy and bulky, and have limited capacity. Lithium-ion batteries are a more expensive option, but they are lightweight, have a high capacity, and have a long cycle life. They are also sensitive to temperature. Nickel-Cadmium batteries are durable, reliable, and have a low self-discharge rate, but they are also expensive and have a short life cycle. Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries offer a high energy density and low cost, but they also have a high self-discharge rate and a short cycle life.
Types of Batteries

| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Batteries | The most common type of battery, lead-acid batteries are robust and inexpensive but have limited recharge cycles. |
| Lithium-ion Batteries | These batteries are lightweight, long-lasting, and have a high energy density but are expensive. |
| Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries | These batteries are known for their long lifecycles, but are expensive and can suffer from memory effect. |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries | NiMH batteries are lighter and more powerful than NiCd batteries, but they are more expensive. |
| Alkaline Batteries | Alkaline batteries are the most common type of disposable battery, but they are not rechargeable. |
| Zinc-Air Batteries | These batteries are lighter and have a higher energy density than alkaline batteries, but are not rechargeable. |
Batteries come in a variety of shapes and sizes and are used to power a wide range of devices. They are typically classified based on the type of chemical compounds used in their construction. Lead-acid batteries are the most common type, but other types such as lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal hydride, alkaline, and zinc-air batteries are also available. Each type has its own pros and cons, so it is important to select the right battery for a particular application.
Advantages of Batteries
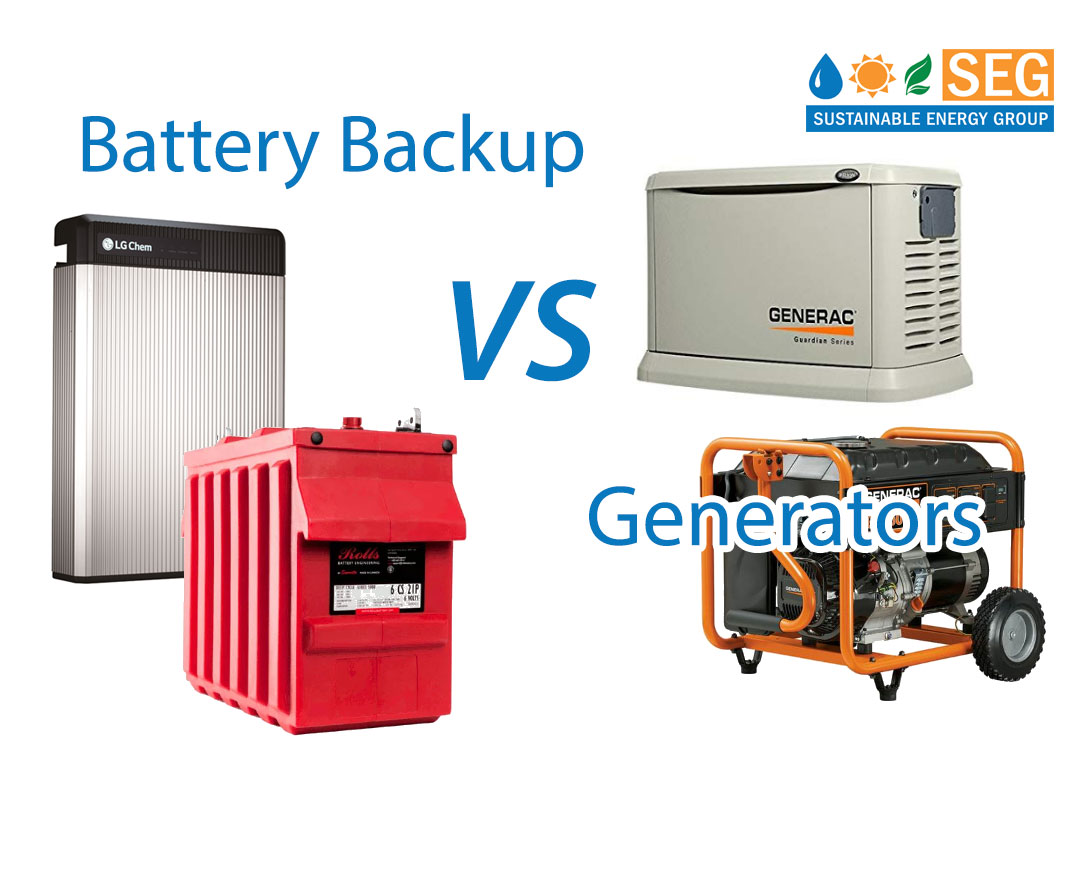
Batteries provide a more efficient and cost-effective option compared to generators. Batteries are relatively maintenance-free and do not require regular refuelling. They are also far quieter than generators, which makes them suitable for use in residential areas. Additionally, they are much smaller and lighter, meaning they can be used in places where a generator would be too bulky or heavy. Batteries are also clean to use, as they do not emit any pollutants or greenhouse gases. This makes them an environmentally friendly option. Furthermore, batteries can be used for multiple purposes, such as providing backup power to homes and businesses, storing energy from solar panels, or powering electric vehicles. Finally, batteries have a much longer lifespan than generators and can last for several years before needing to be replaced.
Disadvantages of Batteries
- Batteries have a limited lifespan and require frequent replacement.
- They have limited power storage capacity, so they must be recharged frequently.
- They can be expensive to purchase, depending on their size and type.
- They can be dangerous due to the risk of leakage, fire and explosion.
- They are affected by temperature and can be damaged if exposed to extreme temperatures.
- They can be heavy and bulky, making them difficult to transport.
Comparison of Generators and Batteries
| Generator | Battery |
|---|---|
| Generators are powered by gasoline, diesel, natural gas or propane. | Batteries are powered by chemical reactions, typically using lithium-ion cells. |
| Generators are typically used for temporary power and can be used to power large appliances and tools. | Batteries are typically used for small electronics and are not suitable for powering large appliances. |
| Generators must be regularly serviced and their fuel must be replenished frequently. | Batteries must be regularly charged and can last for several years before needing to be replaced. |
| Generators are typically more expensive to purchase and operate than batteries. | Batteries are typically less expensive to purchase and operate than generators. |
| Generators emit exhaust and noise, which can be a nuisance. | Batteries are silent and do not emit any exhaust. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of using a battery versus a generator?
Batteries offer increased portability and convenience compared to generators. They are easier to install and require minimal maintenance, as opposed to generators which require fuel and regular maintenance. Batteries are also quieter than generators, making them more suitable for residential areas. Additionally, batteries have no emissions, making them a more environmentally friendly option. Finally, batteries can be charged using solar energy, which can help reduce energy bills and reduce reliance on traditional energy sources.
How Long Do Batteries Last Compared to Generators?
Batteries are a popular alternative to generators, as they are usually more cost-effective and require less maintenance. Batteries usually last an average of about 2-3 years if properly maintained, whereas generators can last for up to 10 years or more with proper maintenance. Batteries also require less space and are lighter and more portable compared to generators. On the other hand, generators are more powerful and can provide a continuous source of energy, while batteries have limited capacity.
What types of applications are best suited for a generator versus a battery?
Generators are primarily used for powering large electrical appliances or devices, such as air conditioners or refrigerators, while batteries are more suitable for powering small electronics, such as cell phones, computers, and tablets. Generators are also better suited for providing a consistent and reliable power source during an emergency, while batteries are best suited for providing short bursts of energy.
What are the Pros and Cons of Running a Generator versus a Battery?
Pros of running a generator include more efficient power production and an easier start-up process. Generators also tend to last longer than batteries, and are more affordable in the long run. On the other hand, batteries are typically quieter and more environmentally friendly than generators. Additionally, batteries have a more limited supply of energy, and require more frequent recharging.
What is the cost difference between a generator and a battery?
The cost of a generator varies greatly depending on the size and type of the unit. A typical generator for home use can cost anywhere from a few hundred dollars to several thousand. On the other hand, batteries are much more cost-effective, with rechargeable models costing anywhere from $60 to $200. In addition, batteries do not require periodic maintenance like generators, resulting in lower long-term costs.
Conclusion
Generators that use a battery are becoming increasingly popular due to their convenience and low maintenance costs. Battery-powered generators are also more environmentally friendly than those that use fuel. However, for larger power needs, such as those for industrial or commercial applications, a traditional fuel-powered generator is still the better choice due to its higher efficiency and power output. Ultimately, the best choice depends on the situation, power requirements, and budget.